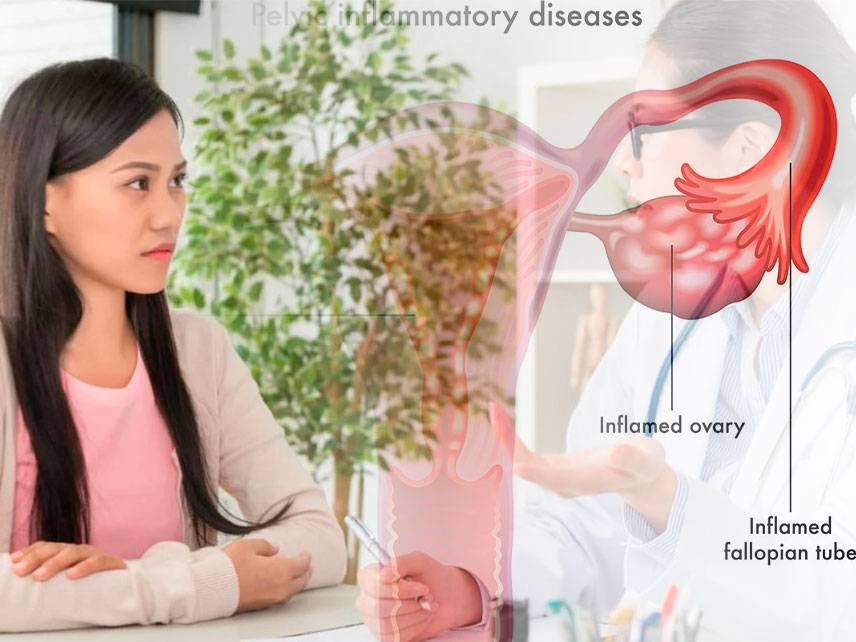
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the reproductive organs in women. It is a serious complication of some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), particularly chlamydia and gonorrhea.
PID can cause permanent damage to the reproductive system and make it difficult or impossible for a woman to have children. It can also lead to chronic pain and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms
PID is a medical emergency. If you think you have PID, you should see a doctor immediately.
Signs and symptoms of PID may include:
-
Abnormal vaginal discharge
-
Fever
-
Pain in the lower abdomen
-
Pain during sex
-
Burning sensation when urinating
-
Nausea
-
Vomiting
If you have any of these symptoms, see a doctor immediately.
Causes
PID is usually caused by bacteria that move from the vagina to the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. The bacteria may be introduced during sexual intercourse, or they may be present in the reproductive tract without causing symptoms (asymptomatic bacteriuria).
The most common bacteria that cause PID are:
-
Chlamydia trachomatis
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
-
Mycoplasma genitalium
These bacteria are usually transmitted through sexual intercourse.
Risk factors
The following factors increase your risk of PID:
-
Multiple sexual partners: This increases your risk of exposure to STDs that can cause PID.
-
Unprotected sex: This increases your risk of exposure to STDs that can cause PID.
-
Previous PID: This increases your risk of reinfection.
-
History of STDs: This increases your risk of exposure to STDs that can cause PID.
-
Smoking: This increases your risk of PID and other reproductive health problems.
Prevention
The best way to prevent PID is to avoid activities that put you at risk of STDs.
This includes:
-
Abstaining from sexual activity
-
Being in a monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested for STDs
-
Using condoms correctly and consistently
If you are sexually active, you should get tested for STDs on a regular basis.
If you have PID, it is important to abstain from sexual activity until the infection has cleared. You should also avoid douching, as this can spread the infection.
Diagnosis
PID is diagnosed based on your symptoms and medical history. Your doctor will also perform a pelvic exam.
During the pelvic exam, your doctor will look for:
-
Tenderness in the lower abdomen
-
Abnormal vaginal discharge
-
Cervical motion tenderness
Your doctor may also order tests to confirm the diagnosis, such as:
-
Pelvic ultrasound
-
CT scan
-
Laparoscopy
Treatment
PID is treated with antibiotics. The type of antibiotic will depend on the bacteria causing the infection.
You will usually need to be hospitalized for treatment. In some cases, you may be able to be treated as an outpatient.
After you have been treated for PID, you should abstain from sexual activity for at least three weeks. You should also avoid douching, as this can spread the infection.
Coping and support
PID can be a difficult and emotional experience. You may feel scared, angry, or alone.
It is important to talk to your doctor about your feelings. You may also benefit from talking to a counselor or joining a support group.
Complications
PID can cause complications, such as:
-
Infertility: PID can damage the fallopian tubes, making it difficult or impossible to get pregnant.
-
Ectopic pregnancy: PID can damage the fallopian tubes, making it more likely for a fertilized egg to implant in the fallopian tube. This is a life-threatening condition.
-
Chronic pelvic pain: PID can cause scarring and inflammation in the reproductive organs, leading to chronic pain.
Living with Pelvic inflammatory disease
PID can be a difficult and emotional experience. You may feel scared, angry, or alone.
It is important to talk to your doctor about your feelings. You may also benefit from talking to a counselor or joining a support group.
After you have been treated for PID, you should abstain from sexual activity for at least three weeks. You should also avoid douching, as this can spread the infection.
If you have PID, it is important to get tested for STDs on a regular basis.
You should also avoid activities that put you at risk of STDs. This includes:
-
Abstaining from sexual activity
-
Being in a monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested for STDs
-
Using condoms correctly and consistently
PID can be a difficult and emotional experience. You may feel scared, angry, or alone. It is important to talk to your doctor about your feelings. You may also benefit from talking to a counselor or joining a support group.