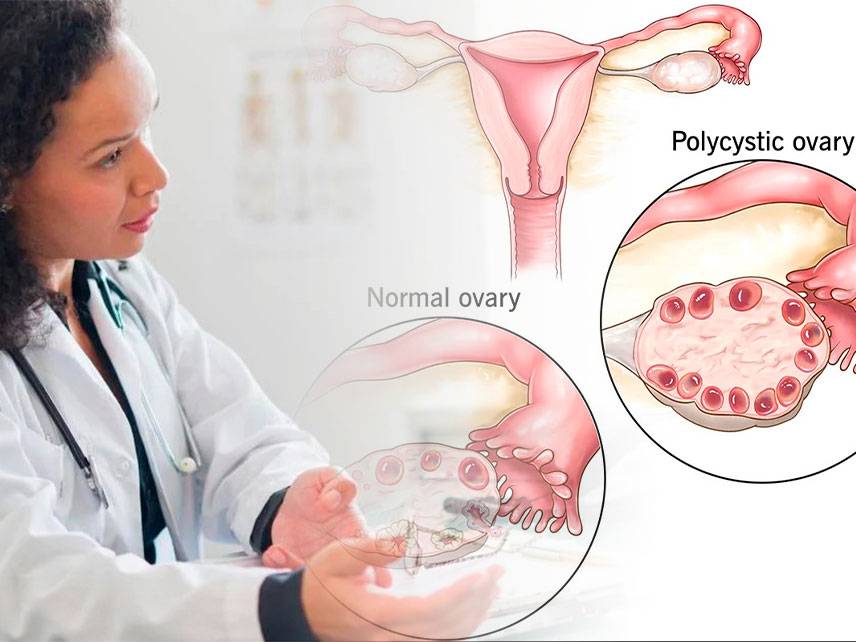
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of childbearing age. The syndrome is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries, irregular menstrual periods, and excess production of male hormones.
Signs and symptoms
PCOS can cause a variety of symptoms, including weight gain, acne, excess hair growth, and fertility problems. Although there is no cure for PCOS, treatment can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
PCOS is a common condition that affects an estimated 5 to 10 percent of women of childbearing age. It is the most common cause of female infertility.
PCOS symptoms can vary from woman to woman. Some women with PCOS have no symptoms, while others may have multiple symptoms.
The most common symptoms of PCOS include:
-
Irregular menstrual periods: Women with PCOS may have infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual periods.
-
Weight gain: PCOS can cause weight gain, due to a combination of insulin resistance and hormonal imbalance.
-
Acne: PCOS can cause acne, due to the presence of excess male hormones.
-
Excess hair growth: PCOS can cause excess hair growth on the face, chest, and back.
-
Fertility problems: PCOS is the most common cause of female infertility.
Causes
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown. However, it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Risk factors
PCOS is a complex condition that has a variety of possible causes. The most likely cause is a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
PCOS is thought to be caused by a combination of:
-
Hormonal imbalance: PCOS is characterized by an imbalance of the hormones insulin, testosterone, and estrogen.
-
Insulin resistance: PCOS is associated with insulin resistance, which is when the body does not respond properly to the hormone insulin.
-
Weight: PCOS is more common in women who are overweight or obese.
Prevention
There are a number of risk factors for PCOS, including:
-
Family history: PCOS is more common in women who have a family history of the condition.
-
Age: PCOS is more common in women of childbearing age.
-
Ethnicity: PCOS is more common in women of Caucasian and Hispanic ethnicity.
There is no sure way to prevent PCOS. However, maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly may help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Diagnosis
PCOS is diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
The most common laboratory tests used to diagnose PCOS include:
-
Blood tests: Blood tests can be used to measure hormone levels and check for insulin resistance.
-
Ultrasound: An ultrasound can be used to check for the presence of ovarian cysts.
Treatment
There is no cure for PCOS. However, treatment can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
The most common treatments for PCOS include:
-
Birth control pills: Birth control pills can help regulate hormone levels and reduce the risk of fertility problems.
-
Anti-androgen medications: Anti-androgen medications can help reduce the symptoms of excess hair growth and acne.
-
Metformin: Metformin is a medication that can help treat insulin resistance.
-
Surgery: Surgery may be an option for women who do not respond to other treatments.
Coping and support
PCOS can cause a variety of physical and emotional symptoms. Coping with these symptoms can be difficult.
There are a number of ways to cope with the symptoms of PCOS, including:
-
Support groups: Support groups can provide emotional support and information about coping with PCOS.
-
Counseling: Counseling can help women deal with the emotional aspects of PCOS.
-
Exercise: Exercise can help manage weight gain and improve insulin resistance.
Complications
PCOS can cause a number of complications, including:
- Infertility: PCOS is the most common cause of female infertility.
- Type 2 diabetes: PCOS can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Heart disease: PCOS can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Endometrial cancer: PCOS can increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
Living with Polycystic ovarian syndrome
PCOS is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on a woman's life. It is important to seek treatment to manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.