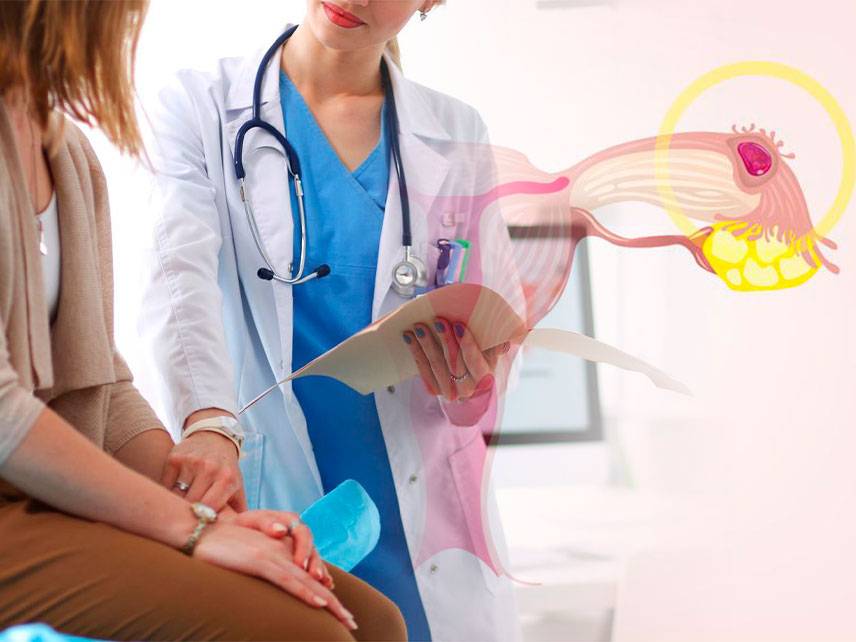
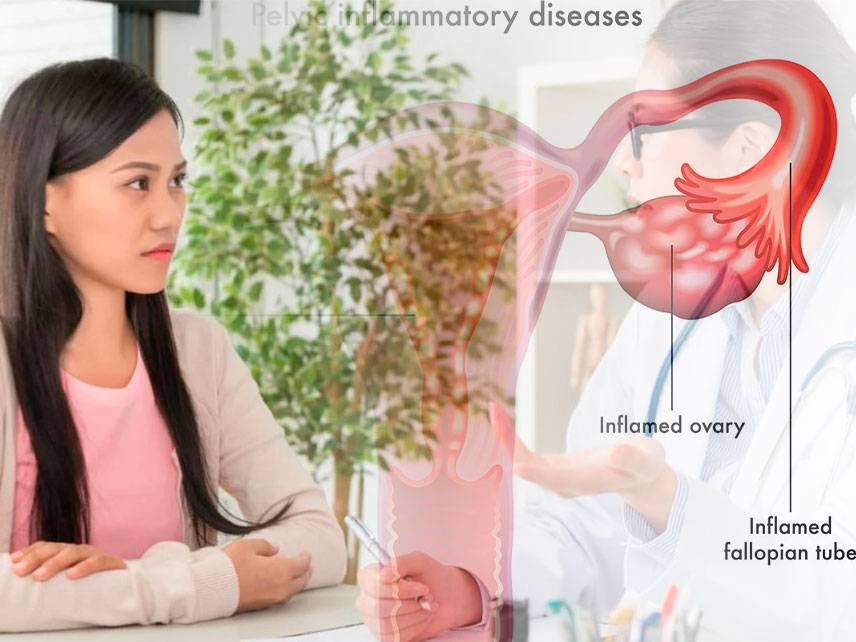
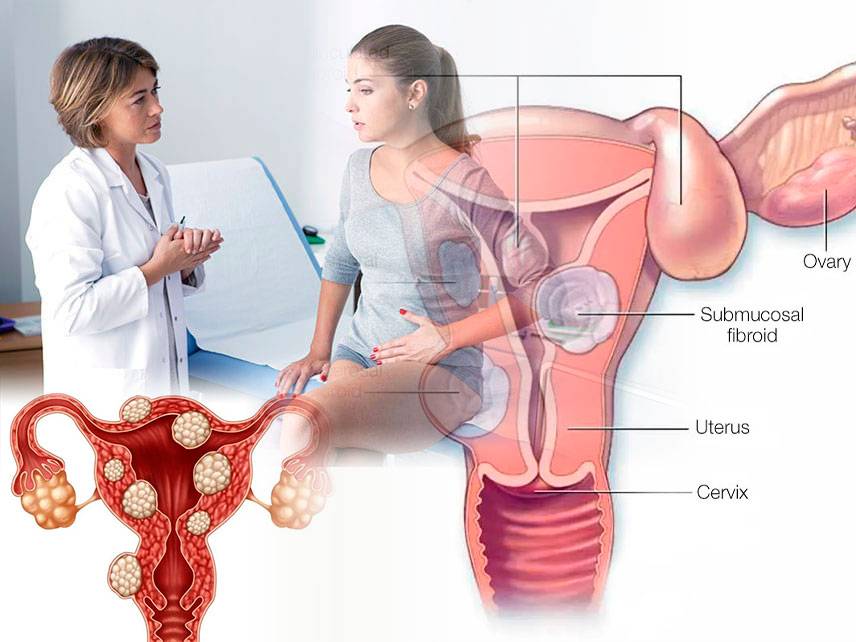
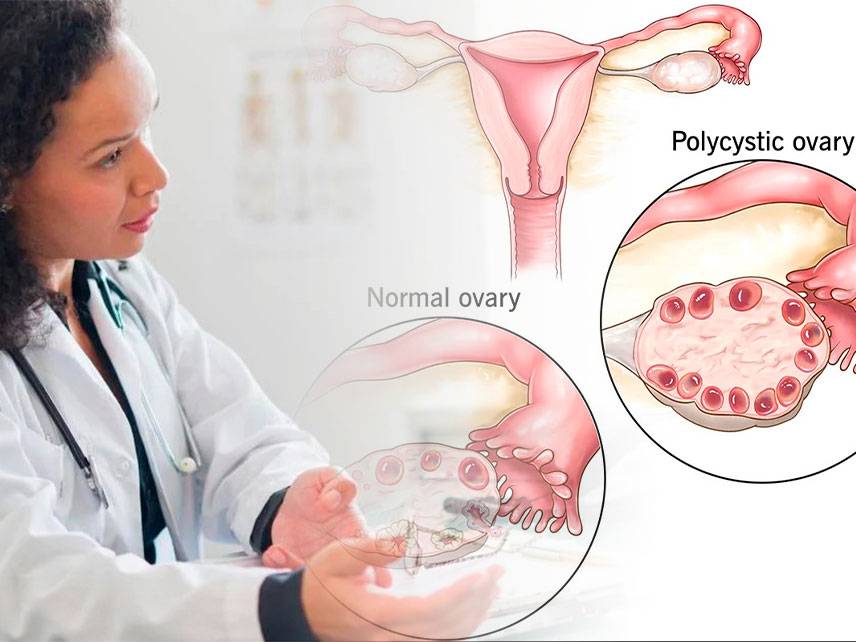
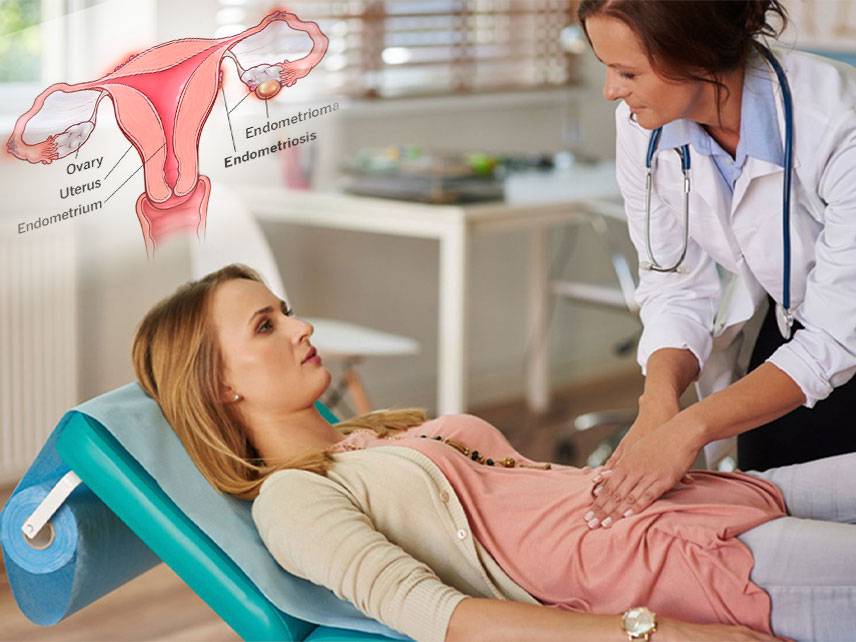
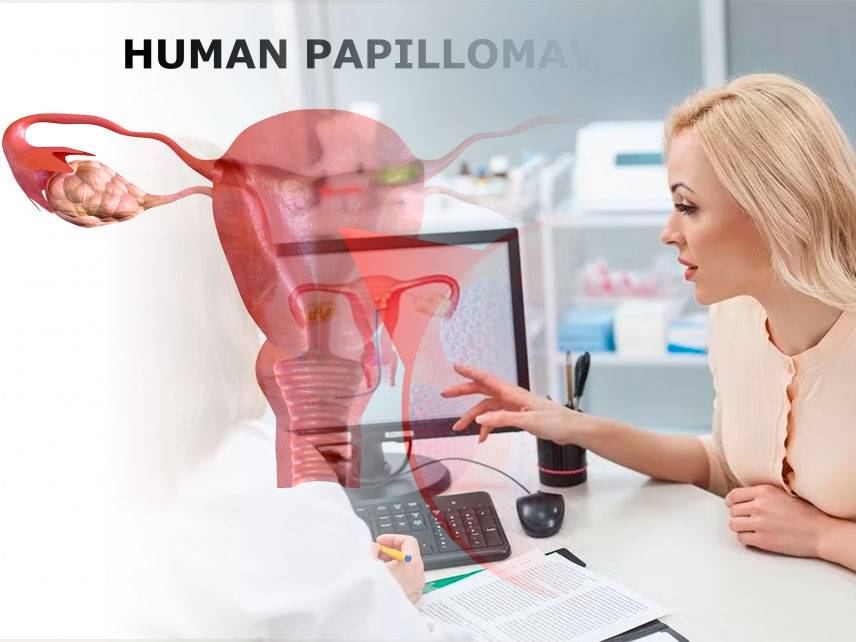
How do I know if I'm having an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, cramping, and nausea. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to contact your doctor immediately. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, order blood tests, and use an ultrasound to determine if you are having an ectopic pregnancy. If the diagnosis is confirmed, a procedure to remove the pregnancy is usually necessary. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, so that you can seek medical help as soon as possible.